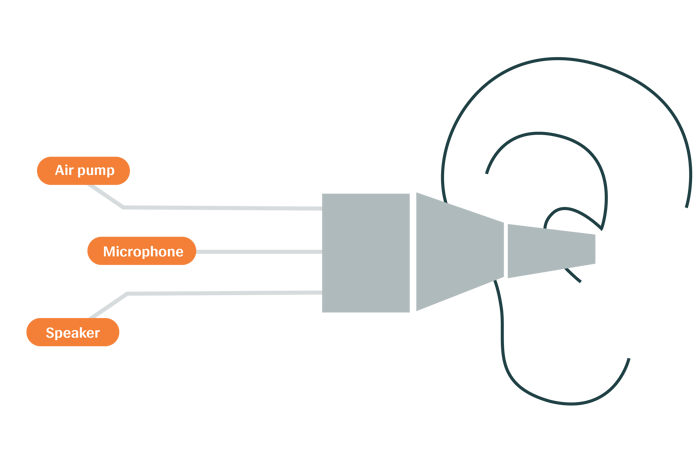
Tympanometry vs Audiometry
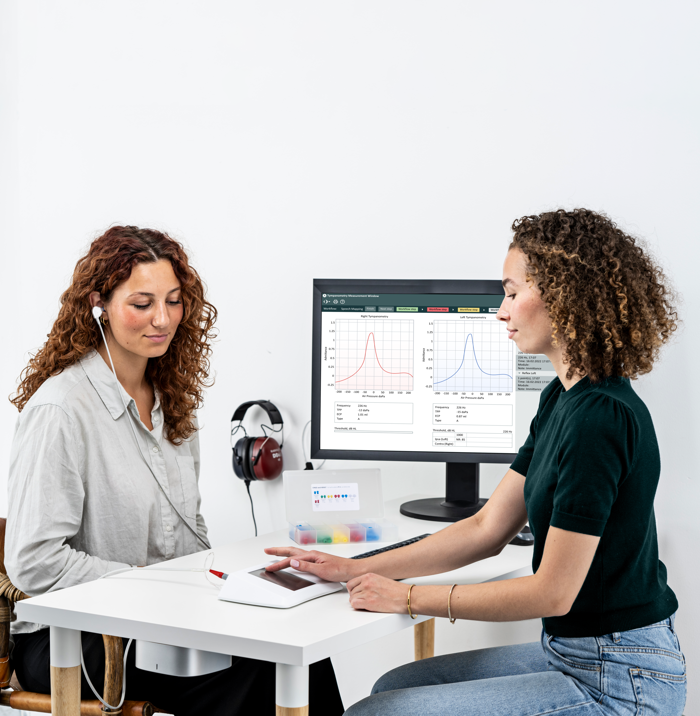
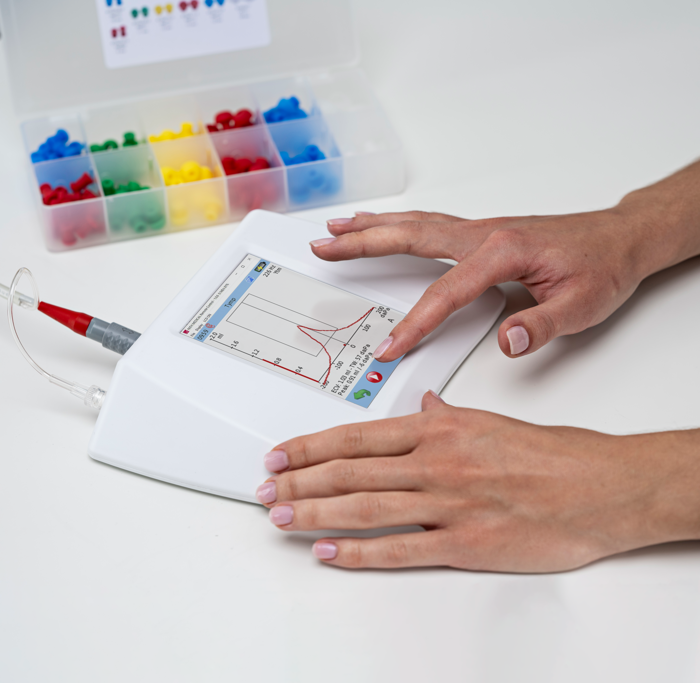
It’s important to note that tympanometry is not a measure of hearing sensitivity and should be used in conjunction with other measures like pure-tone audiometry and speech audiometry to capture a complete view of a patient’s hearing health. It does, however, provide a vast amount of information on middle ear function that a hearing test cannot.
While audiometry is important to determine the severity of hearing loss and to classify conductive, sensorineural, and mixed hearing loss, it cannot determine the cause of conductive and mixed loss. This information can be obtained by performing tympanometry alongside your standard hearing test.
Tympanometry is painless and essentially risk free making it a simple and non-invasive procedure. Additionally, once a seal is achieved by the probe placed in the ear, the measure takes just seconds to complete.